Recent
Business

The Role of Office Supplies in Promoting a Positive Work Environment
Along with technology and furniture, office supplies are essential to an entire workplace environment. Using a reliable office supply vendor can provide convenience and cost savings.
Technology

Understanding High Risk Credit Card Processing: A Comprehensive Guide
High-risk credit card processing is a type of payment processing that is designed for businesses that are considered to be at a higher risk of fraud or chargebacks
Health
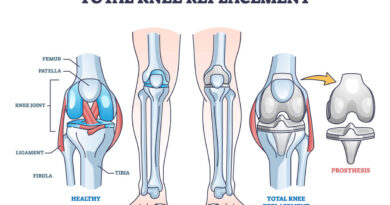
Top 5 Mistakes After Knee Replacement: Skipping Medication
Discover the top Five mistakes to avert after knee replacement surgery. How to optimize your prevent and recover setbacks for a wealthy rehabilitation journey.
Fashion

7 Tips to Dress Your Baby Girl Stylishly
Styling your small girl may be both enjoyable and difficult. On the one hand, it’s an opportunity to dress up your kid in gorgeous clothing and show off their cuteness to the rest of the world. On the other hand, infants grow rapidly, so clothes quickly get too small for them
Crypto

Cryptocurrency Trends: What’s Next in the World of Digital Money
The worldwide of finance is witnessing a paradigm shift fueled with the aid of cryptocurrency. These virtual belongings, constructed at the innovative blockchain generation, are tough traditional economic institutions and reshaping how we apprehend cash.
Finance

The Sassa Status Check For R350: The Complete Guide
SASSA status checks for the R350 grant permit beneficiaries to confirm the progress of their receiving & application timely information.
Recent Posts

Cryptocurrency Trends: What’s Next in the World of Digital Money
The worldwide of finance is witnessing a paradigm shift fueled with the aid of cryptocurrency. These virtual belongings, constructed at the innovative blockchain generation, are tough traditional economic institutions and reshaping how we apprehend cash.




























